Share Important Moment of MileCell Bio with You
2025.11.24
Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells (RPTECs) are specialized cells lining the nephron's proximal tubule[1] , crucial for kidney function. They form a selective barrier and are primarily responsible for the reabsorption of water, ions, and vital nutrients from the glomerular filtrate. These cells also actively secrete[2] [3] organic wastes and drugs, a process driven by specialized transport proteins. Due to these core functions, RPTECs are indispensable in vitro models for studying drug-induced nephrotoxicity, renal transport mechanisms, and the pathophysiology of acute kidney injury and other renal diseases.
ü Guaranteed High Post-Thaw Viability (≥80%)
ü Batch-Specific Certificate of Analysis (COA)
ü Expandable & Culture-Ready Cells
ü Customizable: Multiple Species & Sizes
Cat. No. | Product Description | Size |
BM502-05 | Bama Minipig Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells | 0.5 million |
CY502-05 | Cynomolgus Monkey Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells | 0.5 million |
RM502-05 | Rhesus Monkey Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells | 0.5 million |
BD502-05 | 0.5 million |
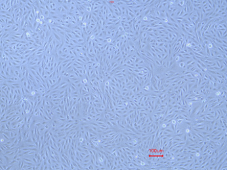
P1
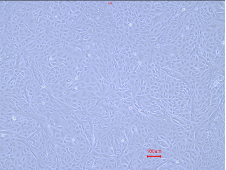
P2
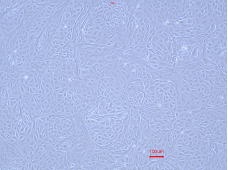
P3
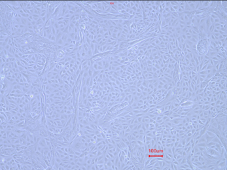
P4
Figure 1:Cyno RPTECs maintained a stable epithelial morphology through early passages (P1-P4). The cells grew as a monolayer with a characteristic cobblestone appearance, distinct cell borders, and visible intercellular connections. Across these passages, the cells demonstrated robust morphological stability without noticeable changes.
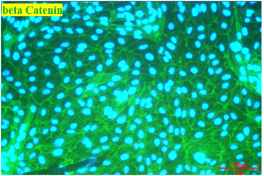
Immunolocalization of β-catenin
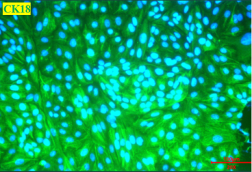
Immunolocalization of CK18
Figure 2:Cyno RPTECs (P2) were cultured for two days and then subjected to immunofluorescence staining. The cells were labeled with specific biomarkers to visualize the expression and localization of β-catenin (green, left) at adherens junctions and cytokeratin 18 (CK18, green, right) in the cytoplasm. The Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue).